Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Definition: An autoimmune disease where your body makes antibodies that attack the cells in your thyroid. This causes the thyroid to under function and not make enough of the thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism).
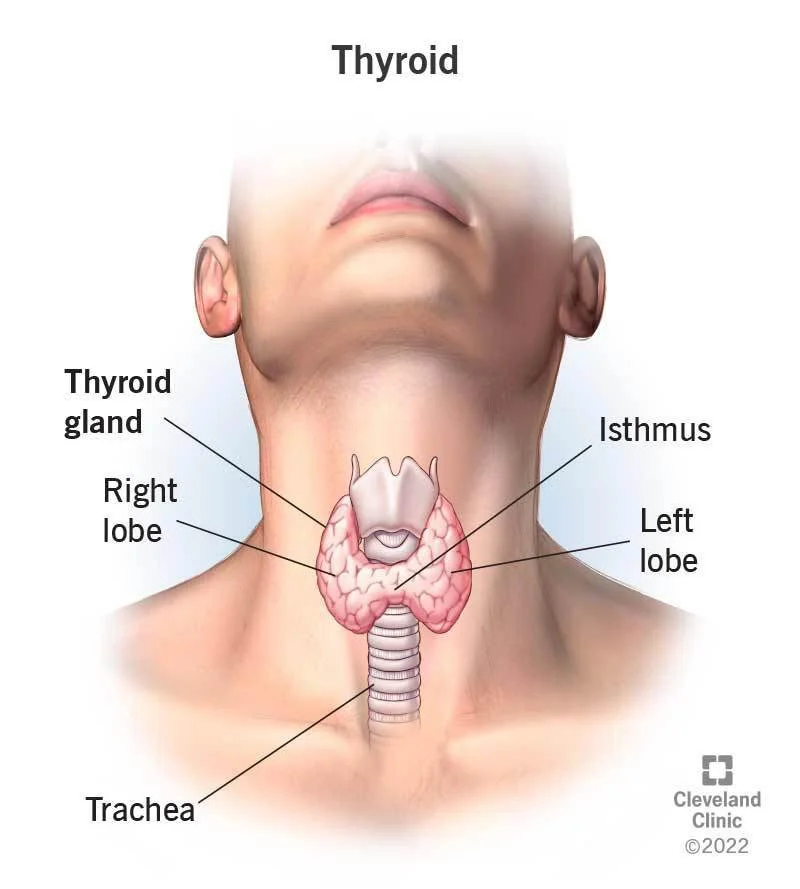
What is a thyroid? The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland in the front of your neck. It produces hormones that control your metabolism - or how your body uses energy.
Note:photograph from:
Thyroid Hormones:
The thyroid produces:
Thyroxine (T4) - the primary hormone your thyroid makes. Once released into the body it is converted to T3.
Triiodothyronine (T3) - your thyroid produces a smaller amount of T3 - but this has a direct affect on your metabolism and does not need to be converted.
Reverse Triiodothyronine (RT3) - your thyroid produces a small amount of this hormone which reverses the effects of T3.
Calcitonin - This hormone regulates the amount of calcium in your blood.
These hormones then affect your: metabolism, heart rate, breathing, digestion, body temperature, brain development, mental activity, skin and bone maintenance, and fertility.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Thyroid disease:
Some will have enlargement of the thyroid gland known as a goiter - or a bulge in the neck. It is not cancerous but it may cause problems with swallowing, breathing or speaking.
Hypothyroidism - low thyroid hormone. When your thyroid cannot produce enough of its hormones due to the damage from antibodies it can cause:
Tiredness
Weight gain
Muscle weakness
Being cold
Depression
Hair and skin changes
Hasitoxicosis- When the thyroid is first attacked by antibodies it may make more hormone (overactive thyroid) - this is called hasitoxicosis. It does not happen to everyone. But if it does you may experience:
Sweating
Rapid heart rate
Heat intolerance
Weight loss
Tremors
Anxiety
Diagnosis: Blood work - your provider will order tests to check your thyroid levels as well as autoantibodies to your thyroid. This will help determine if you need hormone replacement.
Treatment:
Treatment will be based on a number of factors including your age, overall health, medical history, preference(s), how you handle certain medications and treatments and your blood work.
Underactive thyroid can be treated with synthetic thyroid hormone medications which will replace the lost hormone that your thyroid is underproducing which should alleviate the symptoms caused by the decrease in hormone production.
If you have a goiter the medications can help ease the goiter but if the goiter is large enough to cause pain, discomfort, or trouble swallowing, breathing or speaking then you may need surgery to remove the goiter.
Written by: Mallory Stanislawczyk, CRNP, Pediatric Advisor
Sources:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. (2021, August 8). Johns Hopkins Medicine. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/hashimotos-thyroiditis
Professional, C. C. M. (2022, June 7). Thyroid. Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23188-thyroid